LoRaWAN Protocol: Everything You Need to Know


LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is currently at the forefront of innovation in the Internet of Things (IoT) domain, especially for building-related applications. This network protocol stands out for its low energy consumption and extended range, two major advantages that significantly enhance the performance of IoT devices.
In a world where connectivity and energy efficiency are paramount, LoRaWAN offers an optimal solution for a multitude of IoT scenarios, ranging from environmental monitoring to intelligent building management. This article delves into the technical details and practical applications of LoRaWAN, providing an in-depth understanding of this protocol and its impact on today's connected world.
If you want to understand in more detail what this protocol entails and what its specifications are, you'll find all the information you need in this article!
The Wattsense Solution makes integrating LoRaWAN technology into buildings simple, fast, and affordable. Feel free to request your demonstration to learn more.
What is LoRaWAN?

LoRaWAN is a Low Power, Wide Area Network (LPWAN) protocol designed to wirelessly connect battery-operated IoT devices to regional, national, or global networks.
The LoRaWAN protocol was developed in 2009 by the founders of the Grenoble-based company Cycléo, which was acquired by Semtech in 2012. Three years later, Semtech founded the LoRa Alliance.
The LoRa Alliance
The LoRa Alliance is an industry association that now has over 500 members, including IoT product and service providers, manufacturers, and telecommunications companies. The LoRa Alliance is a major player in the IoT ecosystem, significantly contributing to the growth and adoption of LoRaWAN technology worldwide. It organizes events, provides training, manages a certification program, and actively develops the LoRaWAN ecosystem for various IoT applications, from urban management to agriculture.
Read: LoRa vs LoRaWAN: What are the Differences?
How does LoRaWAN work?
Signal Range
LoRaWAN is known for its ability to provide long-distance communication, often far beyond that of traditional wireless networks. This extended range makes it ideal for applications in extensive areas, including rural or urban areas, with the ability to cover kilometers.
A single LoRaWAN antenna can effectively cover a large area, ranging from 3000 to 5000 square meters, which is ideal for use in medium and large buildings. LoRaWAN technology ensures reliable communication with sensors placed on different floors, including areas that are typically hard to reach, such as basements.
Signal Adaptability and Spreading Factor
LoRaWAN also distinguishes itself by its ability to effectively adjust the signal power, thereby improving range while minimizing energy consumption. This efficiency is achieved through dynamic adjustment of the Spreading Factor (SF), which adapts according to the transmission environment conditions. This ensures efficient signal transmission, even through obstacles, while preserving the battery life of the sensors. This aspect of LoRaWAN is particularly beneficial for modernization projects in existing buildings where signal transmission can be challenging.
"Wattsense offers a private LoRaWAN solution, which allows being closer to LoRaWAN equipment, resulting in a lower spreading factor and thus improving their lifespan and reducing latency."
Read: Monitor building technical equipment using LoRaWAN: A solution to wiring issues.
Energy Consumption
LoRaWAN devices, designed for low energy consumption, offer up to 10 years of battery life, which is ideal for applications where frequent battery replacement is difficult or costly. On the market, a wide range of LoRaWAN sensors is available to monitor various parameters in buildings, such as temperature, humidity, and energy consumption. The LoRaWAN ecosystem includes three equipment classes, balancing energy consumption and continuous communication.
Class A sensors, for example, are highly energy-efficient, activating briefly for measurements and communications, and ideal for battery-dependent applications. Class C sensors, on the other hand, are in constant listening mode and consume more power, usually connected to an external power source.
Here are some use cases for Class A and C devices:
- Creating simple heating regulations using a thermostatic valve.
- Controlling ON/OFF relays using dry-contact sensors. In these examples, for reactive regulation or quick ON/OFF, you would use Class C devices.
Latency and Transmission
Usually, LoRaWAN latency is slightly higher compared to cellular networks but remains adequate for many IoT applications that do not require instant transmission. It is important to note that latency may vary slightly depending on the type of sensor used. For a Class C sensor, a command (downlink) is sent as soon as it is programmed, and there is no latency. With a Class A sensor, commands are sent in response to a message previously sent by the sensor to the server.
Data Rate
The data rate in LoRaWAN typically ranges from 0.3 kbps to 50 kbps. This range is suitable for transmitting small amounts of data, typical of IoT applications, where payload sizes range from 51 to 241 bytes.
Flexibility of LoRaWAN Network: Private or Public LoRaWAN Network
Advantages and Disadvantages of LoRaWAN

Advantages of LoRaWAN
Cost Savings
Reduced sensor and infrastructure costs. LoRaWAN gateways are economical and require fewer units compared to other wireless protocols.
Sensor Diversity
Proven and widely adopted technology, offering a wide range of sensors suitable for various IoT applications
Simplified Programming
Minimizes the need for complex programming, making implementation easier.
Wireless Solution
Eliminates issues related to wiring, ideal for renovations and installations in complex locations.
Low Power Consumption and Long Range
Ideal for IoT solutions requiring low power consumption and extensive coverage.
Network Flexibility
Compatible with both public and private networks, offering excellent signal penetration even in underground environments
Tracking and Geolocation
Allows for real-time tracking services without requiring GPS chips.
Disadvantages of LoRaWAN
Bidirectional Management
Complexities in programming and commissioning due to encoding, throughput, and latency in the case of Class A sensors.
Latency
Latency time can be significant depending on the type of sensor and may limit certain applications.
Limitation for Large Payloads
Less suitable for applications requiring high data throughput and does not support multimedia files.
LoRaWAN: Highly Suitable for Technical Management and Building Performance

LoRaWAN proves to be particularly effective for technical management and improving building performance. The use of IoT technologies communicating via LoRaWAN – such as sensors, equipment, and LoRaWAN gateways – is a great way to easily, quickly, and without heavy construction work integrate smart building technologies or modernize building technical management. In other words, thanks to LoRaWAN, it becomes simpler and more cost-effective to implement energy efficiency strategies, improve occupant comfort, and reduce maintenance costs, synergizing with other technologies.
A turnkey LoRaWAN solution
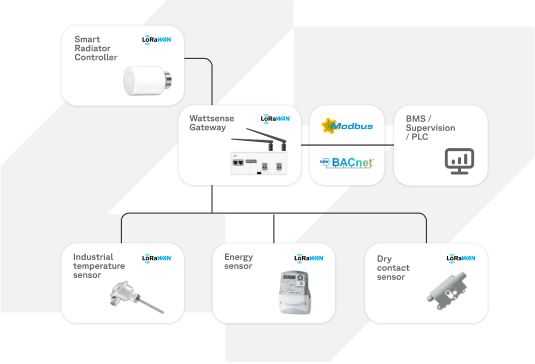
The Wattsense solution enables interoperability and the integration of IoT solutions with local building management systems and digital services.
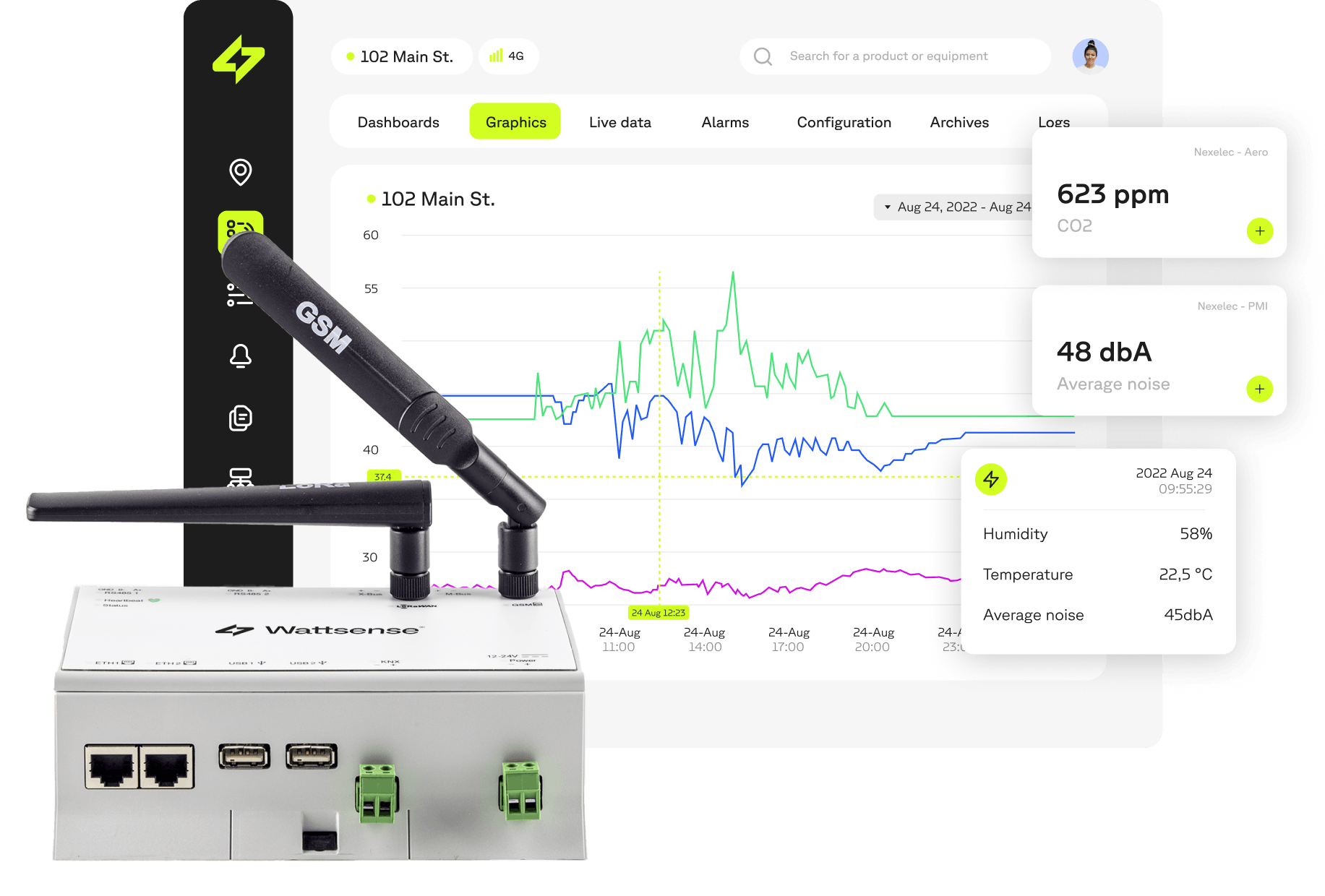
Wattsense's connectivity solution converts LoRaWAN data into BACnet IP/Modbus IP, allowing you to locally access data from any LoRaWAN sensor and deploy Smart Building solutions rapidly, with great flexibility.
Practical Applications of LoRaWAN in Buildings
- Energy Monitoring: Management and tracking of energy consumption via meters and individualization of heating costs.
- Cold Chain Monitoring: Crucial monitoring of temperatures in sensitive storage areas, such as refrigerators and cold rooms, to ensure proper preservation of temperature-sensitive products, essential in the food and health sectors.
- Air and Water Quality: Use of advanced sensors for continuous monitoring of CO2 levels and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), ensuring a healthy environment compliant with standards.
- Comfort: Temperature and humidity control for optimal indoor environment, contributing to a more pleasant working or living environment.
- Maintenance: Implementation of alarms and use of meters for remote reading, use of dry contacts for equipment fault recovery (AHUs, chillers, boilers, etc.). For example, it's possible to install LoRaWAN water leak detection sensors.
- Building Renovation: Seamless integration of modern equipment into existing Building Management Systems (BMS), allowing technological upgrades without complex wired installations to comply with various regulations such as the tertiary decree or the BACS decree. For example, installing actuators like dry contacts and communicating thermostatic valves.
- Security and Other Applications: Enhancement of security and other functionalities beyond pure technical management.
Read: LoRaWAN project best practices
In Conclusion
The LoRaWAN communication protocol is a long-range, low-power wireless protocol designed to connect objects to the Internet, such as IoT sensors in environments where traditional cellular connectivity is not possible or costly. It's an efficient and sustainable solution for Smart Buildings due to its longevity and cost-effectiveness and can improve energy performance, comfort, air quality, security, or equipment management of a building.
Want to learn more about the Wattsense connectivity solution?
Discover our solutionContinue reading

How PropTechs accelerate their growth using IoT connectivity solutions