Maintaining a building ensures its durability, energy efficiency and the comfort of its occupants. Breakdowns, unforeseen damage and ageing equipment and materials inevitably lead to deterioration of the building and its interior. So it's essential to keep them in good condition.
The different types of maintenance
There are three main types of maintenance commonly used in the construction industry:
- Corrective or curative maintenance
- Preventive maintenance
- Predictive maintenance
Corrective maintenance is carried out after a breakdown or malfunction has occurred, often as a matter of urgency.
Preventive maintenance, on the other hand, is carried out according to a predefined schedule, based on knowledge of the theoretical wear and tear of the equipment; the aim is to intervene before a breakdown occurs.
That leaves predictive maintenance, which, far from replacing the previous two, is on the contrary a recent and highly effective complement.
Definition of predictive maintenance
Predictive maintenance is distinguished by its ability to prevent breakdowns and predict when equipment failure may occur.
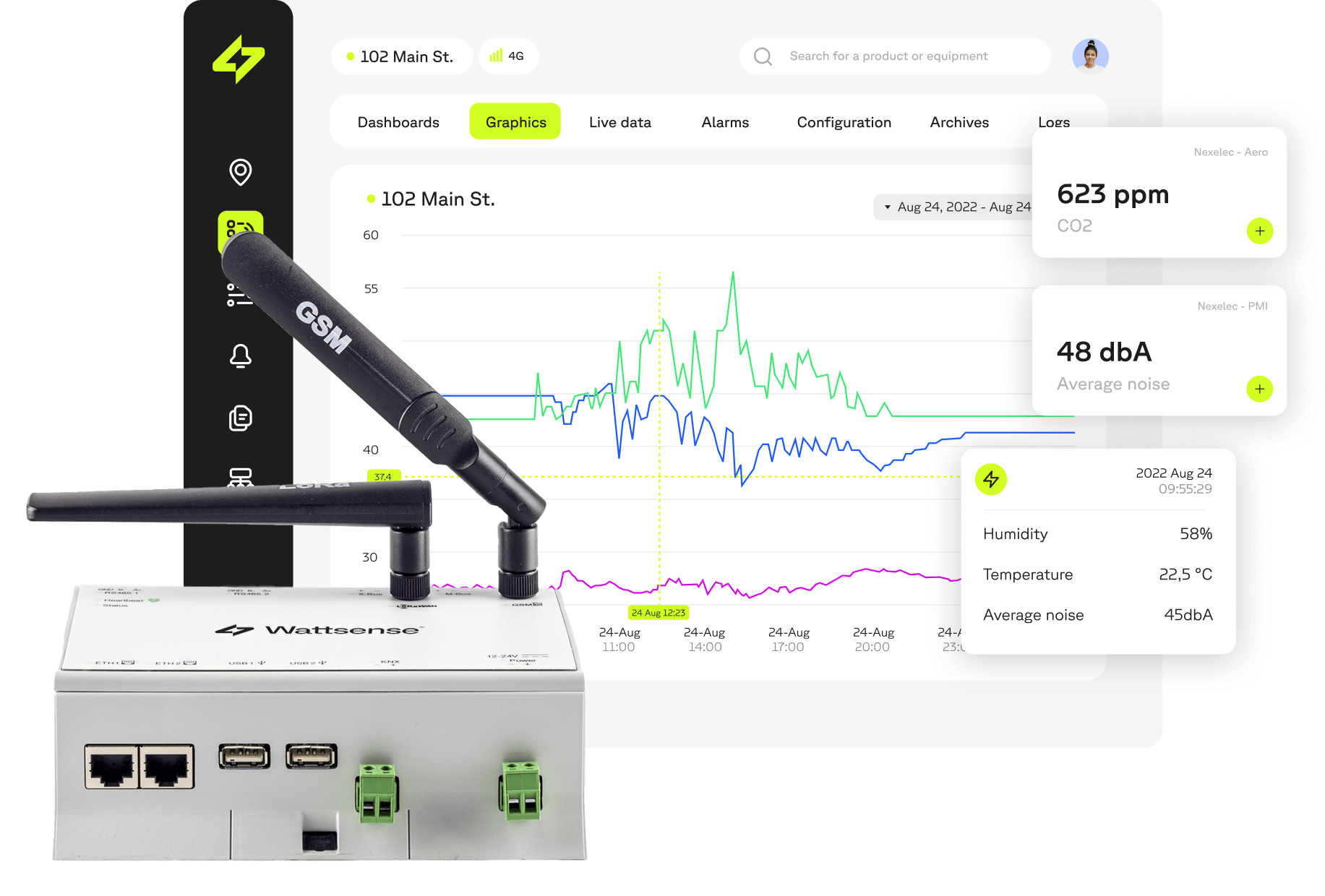
Predictive maintenance benefits from technological advances such as IoT (Internet of Things) devices combined with connectivity solutions and SaaS platforms. These technologies enable real-time analysis of data and the use of remote alarms to spot the warning signs of equipment failure.
This proactive approach makes it possible to anticipate breakdowns by planning maintenance operations in advance. By transmitting alerts remotely when risky equipment behaviour is detected, teams can act quickly to resolve problems before they become critical, ensuring continuity of operations.
In the building sector, predictive maintenance can be applied to any system, such as heating, ventilation and air conditioning (HVAC), lighting or lift operation. Automating and centralising data in a connected management system enables real-time monitoring and rapid intervention.
Predictive maintenance made easy
Our connectivity solution centralises data, enabling it to be viewed in real-time and remote alarms to be set up for intelligent, remote management of building maintenance. All without major works, equipment changes or additional complexity.
The benefits of advanced predictive maintenance
The adoption of predictive maintenance in building management is an undeniable step forward. It
- It considerably reduces maintenance costs by avoiding costly emergency interventions, while helping to extend the lifespan of equipment.
- By identifying minor malfunctions, it can be used to improve performance without human intervention, using adjustments, resulting in more energy-efficient buildings, greater comfort and greater safety. It also reduces the amount of human time spent on maintenance.