The Modbus protocol in building management


Modbus is a standard open communication protocol used to establish client-server communication between intelligent devices.
Modbus was created in 1979 by Modican for use with Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC). It uses a Master/Slave architecture where the device requesting the information is called the Modbus Master, and the devices supplying information are Modbus Slaves. The Master can also write information to the Slaves.
The Modbus protocol is one of the most used protocols in the building sector to transmit information from control devices to the central controller that can be used as a data-gathering system. Its uses are with Building Management Systems (BMS) and Industrial Automation Systems (IAS).
This protocol primarily uses RS-232 or RS-485 serial interfaces for communications; it connects a supervisory computer with a remote terminal unit (RTU) and data acquisition with SCADA software. These characteristics make it easy to integrate with building equipment and control applications.
There is the Modbus RTU for serial lines, and for Ethernet connections, the Modbus TCP.
The advantage of Modbus in building management
- Open protocol, it avoids royalty payments for users.
- Simple to use.
- No need for RAM space. In the early days, this feature was key when processors used 8-bit technology, and RAM and ROM resources were more expensive and challenging to acquire.
- Message checking with low transmission errors and 99% accuracy.
Modbus TCP Server

The Modbus data communication protocol is one of the most commonly used protocols in the building management sector. It was initially developed for Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC).
Such as Modbus RTU or ASCII, Modbus TCP is a variant of the Modbus protocol. Modbus TCP is a communication protocol that allows two or more devices to communicate via an IP network. Unlike Modbus serial link, Modbus TCP is not based on a hierarchical structure but a client/server model.
Modbus TCP is an open Industrial IP network specified as an RFC Internet standard. It can also be known as Modbus TCP/IP.
The transfer of information between a Modbus client and server starts when:

- The client sends a request to the server to transfer data, execute a command, or perform one of many other possible functions.

2. After the server receives the request, it runs the command or recuperates the required data from its memory.
3. The server then answers the client by acknowledging that the command is complete or offering the requested data.
The Modbus TCP functionality implements both client and server services to initiate communications with other controllers and I/O devices and respond to requests from other controllers, SCADA, and other equipment or supervisory systems.
Without any configuration, the controller's embedded Ethernet port supports Modbus Server and does not require extra programming tactics from the user.
Modbus TCP to LoRaWAN functionality
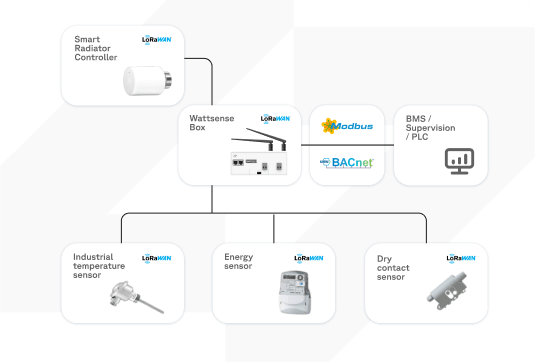
Wattsense is an IoT solution dedicated to facilitating BMS integration and quickly connecting technical assets. We have developed the Bridge, an intuitive IoT gateway and powerful controller to simplify BMS integration.
The LoRaWAN to Modbus TCP function allows users to locally collect data on any sensor such as consumed electricity, water, gas, air quality, temperature, or even other building parameters which otherwise have to be checked separately.
The functionality centralizes information with a complete system overview displayed in our user-friendly console, or it can also be redirected to your preferred supervision system, such as SCADA.
The Wattsense LoRaWAN to Modbus functionality implements a Modbus TCP Server communication. Learn more about the LoRaWAN and Modbus functionality.
For more information about connecting your Modbus equipment with the Wattsense IoT, write us at: contact@wattsense.com
Other Modbus resources

When building the appropriate set of parameters for Modbus configuration, an interesting device is the TicMaster Modbus teleinfo gatewayModbus teleinfo gateway by Antarc Automation.
The TicMaster® is an intelligent gateway for the acquisition of customer tele-information signals (TIC) broadcasted by Enedis electronic meters. It offers from 2 to 10 TIC inputs allowing it to follow simultaneously as many meters. It is compatible with all Blue (CBE), Linky, Yellow (CJE), Green (Emerald) (ICE), SME-SMI, and SAPHIR meters.
The commissioning is fully automatic and does not require any action from the user.
The integration in the IoT Box is immediate, thanks to predefined templates.
The host interface is either Modbus RTU or TCP.
Want to learn more about the Wattsense connectivity solution?
Discover our solutionContinue reading