Monitor the technical equipment of a building through LoRaWAN: A Solution to Wiring Issues

In the ever-evolving world of technical building management, industry players face significant technical challenges. Energy efficiency, compliance with regulations, and improving occupant comfort are crucial objectives.
However, the reality of existing buildings often presents unique challenges, especially when it is impossible to install new cables to collect data from technical equipment.
In these complex situations, the use of wireless protocols, especially the LoRaWAN communication protocol, proves to be a clever solution, whether the equipment is already installed in the building or not.
Discover in this article why LoRaWAN is the most suitable alternative to wired protocols for gathering equipment data when cable installation is impossible in the environment. Learn how it ensures the success of building technical management renovation or modernization projects.
The Wattsense connectivity solution converts LoRaWAN data to BACnet/ Modbus so you can locally access the data of any sensor and deploy Smart Building solutions quickly. Find out more here.
Challenges in data management for existing buildings
One of the current major challenges in the building management sector is the implementation of a data supervision system to comply with existing regulations and address new challenges in building energy improvement, such as the tertiary decree, the BACS decree, or the BAT-TH-116 decree. However, projects aiming to modernize or renovate existing buildings often encounter significant practical obstacles that impede data supervision, such as restricted roof access, obstructed cable pathways, complex recovery of ventilation ducts, and the implementation of automatic radiator regulation using thermostatic valves.
Do these situations sound familiar to you? Indeed, they are common and underscore the limitations of wired solutions in certain usage scenarios. The recommended alternative to efficiently and reliably collect equipment data in such situations is the use of wireless protocols, which, due to their nature, circumvent certain physical constraints of the building.
While wireless solutions have earned a reputation for being less reliable than their wired counterparts, recent technological advances now make them nearly as robust and dependable as wired protocols.

EnOcean : offers remarkably low bidirectionality and latency, meaning devices can communicate efficiently in both directions with nearly instant response. However, this protocol often requires a large number of gateways to cover extensive areas, which can be costly and complex in terms of architecture.

Zigbee : This protocol operates in a mesh network, where each device (node) is both a transmitter and a receiver. Adding a new device extends the network's range and strengthens its structure. This allows for reliable coverage even in complex environments, such as large buildings. However, there are limited options for devices compatible with this protocol, and its energy consumption is relatively high (sensors/actuators are constantly in transmit/receive mode), making it less suitable for complex renovation projects.

Sigfox : While standing out for its extensive coverage, low infrastructure cost, and data provision via an API in the cloud, it does not always efficiently meet the needs of building technical management, which require local communication. Sigfox is an operated network, making it difficult to establish a private network.

LoRaWAN : The LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) protocol is a wireless communication technology designed to enable data transmission over long distances while consuming minimal energy. Primarily suitable for Internet of Things (IoT) applications, the LoRaWAN protocol offers significant advantages in the field of building technical management. Unlike Sigfox, it is available in a private version and allows for local reporting of information from technical installations.
The use of the LoRaWAN protocol has proven to be extremely suitable for collecting data from sensors and meters. However, when it comes to actuators, the decision needs to be examined more closely, taking into account the specific circumstances of each case.
To address energy monitoring and air quality issues, LoRaWAN technology seems to us to be the wireless protocol best suited to building constraints, especially in situations involving a large number of devices to be monitored and controlled, which is often the case in BACS compliance projects or upgrades to Class B BMS.
Advantages of the LoRaWAN protocol
The integration of the LoRaWAN protocol into building technical management system creation or renovation projects opens exceptional opportunities to improve energy efficiency, ensure compliance with standards, and simplify the installation and commissioning process.
Cable-Free Installation
One of the key strengths of LoRaWAN technology lies in its ability to be deployed without the need for complex cable installation. This feature is particularly relevant in the context of renovation, where access to certain areas may be limited by architectural or technical constraints. LoRaWAN sensors or equipment can be quickly installed without altering the existing structure and maintaining the aesthetics of the location, thereby reducing costs, timelines, and disruptions associated with traditional wiring work.
Wide Range of Equipment
There is currently a variety of LoRaWAN equipment available on the market for monitoring and data collection in buildings. These sensors can be used to monitor temperature, humidity, air quality, lighting, energy consumption, motion detection, and many other parameters.
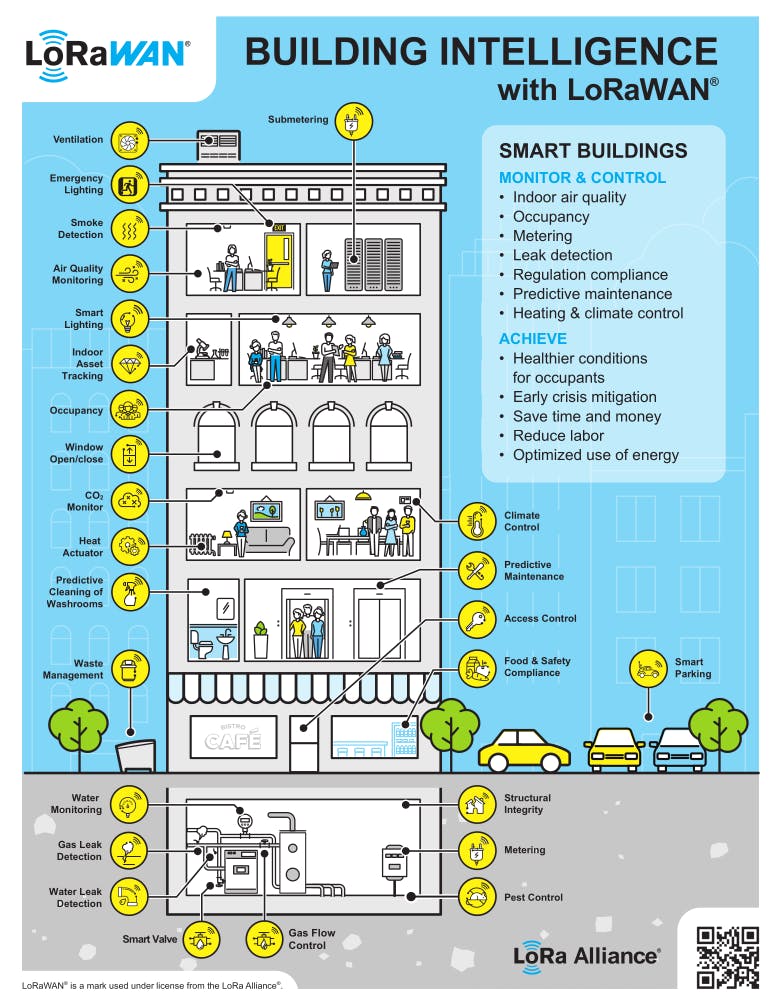
Source : https://lora-alliance.org/
The availability of these devices varies by region and supplier, but in general, there is a wide range of products suitable for various building technical management applications.
The LoRaWAN ecosystem currently offers three classes of devices, each providing a trade-off between energy consumption and communication continuity. The most common ones are as follows:
- Class A sensors stand out for their high energy efficiency. They spend the majority of their time in a sleep state and wake up periodically to perform measurements, transmit data, briefly listen for commands from their gateway, and then return to sleep mode until the next measurement. This characteristic makes them a perfect choice for applications relying on battery-powered sensors.
- Class C sensors operate in a constant listening mode. Consequently, they consume more energy than Class A sensors. Therefore, they are most often connected to an external power source.
Adaptability and range of the LoRaWAN signal
A major advantage of LoRaWAN lies in its ability to intelligently adjust signal power to optimize coverage while minimizing energy consumption. This capability is made possible by the automatic adjustment of the "spreading factor" (SF) based on transmission conditions. This adaptation ensures optimal penetration through obstacles without overexploiting sensor batteries. Once again, LoRaWAN proves particularly well-suited for renovation projects where existing structures can pose challenges to signal transmission.
With the LoRaWAN gateway feature in the Wattsense connectivity solution, the calculation of the spreading factor is simplified through the evaluation of the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and the Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI). This functionality ensures optimal operation of LoRaWAN sensors by automatically adjusting transmission parameters.
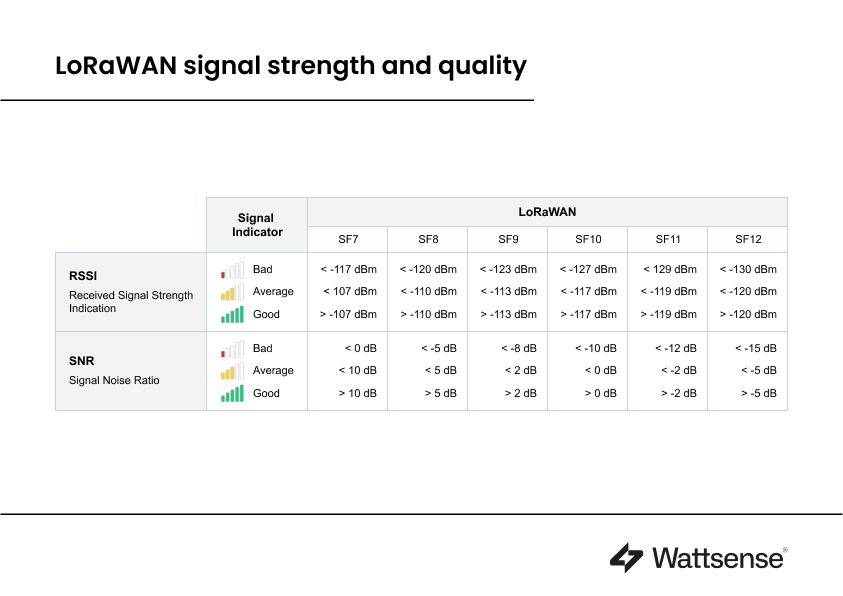
Another significant advantage of the LoRaWAN communication protocol is its range. Data can be collected from sensors located at significant distances (up to a radius of 800 meters) from the gateway, which is particularly advantageous for large-scale buildings. Indeed, a single antenna is sufficient to cover a building of 3000 to 5000 square meters. It allows for the capture of data from sensors installed on different floors of the building, and sometimes even in basements.
The LoRaWAN technology enables reliable communication even in complex environments, ensuring the accurate collection of data necessary for building technical management.
Decoding a LoRaWAN Frame
The process of decoding LoRaWAN frames may seem intricate, but it is crucial for understanding the transmitted data. Here is a basic illustration to better visualize this concept:
A LoRaWAN frame is essentially a data packet containing information collected by a sensor or intended for a LoRaWAN-compatible device. These frames can be transmitted in an upward direction (uplink) from sensors to a LoRaWAN gateway or in a downward direction (downlink) to configure or activate specific functionalities. Each manufacturer provides specific decoding instructions for each type of frame, explaining how the data is structured and how to extract it. Note that the decoding process differs for uplink and downlink frames.
Decoding uplink frames
Example of a LoRaWAN up link frame :
A60100200400C6C9E00005C400000000009AD640154800000000000020:56
When a sensor sends data to a LoRaWAN gateway, the uplink frame contains the necessary information to identify and interpret the captured values. Typically, this involves taking the raw data from the sensor and sending it to a programming tool such as Node-RED. You can then create your own program to decode the frame. Some LoRaWAN gateways, like the Wattsense solution, also integrate a codec to decode the raw data, providing a convenient option.
Simplified Decoding with Wattsense (Uplink Codec):
Wattsense significantly streamlines this task by automatically decoding frames from over 400 LoRaWAN devices available in the market. After sensor installation,
technical teams can retrieve specific variables of interest with just a few clicks.
Decoding Downlink Frames
Example of a LoRaWAN downlink frame :
0E13:1
Regarding downlink frames, the goal is to send configuration parameters to LoRaWAN devices. This is typically used for the initial setup or commissioning of devices. However, this process is more complex due to the encoding and generation of required codes. Many manufacturers also provide downlink code generators on their websites, making the creation of configuration parameters more straightforward.
Specific Case of Actuators (Vicky and Micropelt Thermostatic Valves) :
Source : https://www.rg2i.com/vanne-thermostatique-lorawan/
For devices such as actuators, like thermostatic valves, LoRaWAN offers the possibility to implement regular actions, such as adjusting a setpoint or activating a contactor.
To simplify the integration of this type of equipment into a Building Management System (BMS), at Wattsense, we have decoded the ambient temperature setpoint variable for writing. Therefore, to change the ambient temperature setpoint, you only need to write the desired temperature value.
Seamless Integration of LoRaWAN Technology into an Existing BMS
With a multiprotocol connectivity solution like Wattsense, the conversion of data into standard protocols such as BACnet is exceptionally straightforward. This step is crucial for linking the collected data to existing Building Management Systems (BMS), thereby creating a seamless integration with other building equipment.
Savings achieved through the use of the LoRaWAN communication protocol
One of the most attractive aspects of using LoRaWAN equipment in building management lies in the substantial savings it enables. These savings manifest both in reduced wiring costs and minimized programming efforts, thereby enhancing the cost-effectiveness of renovation projects.
Calculating Savings
One of the primary sources of savings comes from the significant reduction in the wiring needed to connect various sensors and equipment. Compared to traditional methods that require complex cable installation, the use of LoRaWAN equipment bypasses this costly and time-consuming step. This results in decreased costs related to materials, labor, and working hours, significantly lightening the overall project budget.
Minimization of Programming Efforts
Another source of savings lies in reducing the programming efforts required to implement building management systems. LoRaWAN equipment, especially when integrated into the Wattsense solution, offers a simplified and intuitive configuration. With features like automated decoding of LoRaWAN frames and pre-configuration for over 400 LoRaWAN devices, tedious programming tasks are significantly reduced. This automation saves time and cuts costs associated with training and maintaining advanced technical skills.
Cost-Effectiveness of Renovation Projects
The savings achieved through the use of LoRaWAN technology directly contribute to the cost-effectiveness of renovation projects in building management. By reducing expenses related to wiring and programming, various project stakeholders can optimize the use of their financial resources while ensuring an efficient and rapid implementation of solutions.
Example: Monitoring CO2 Levels in a Primary School Project
Objective: Ensure Sufficient Supply of Hygienic Air in 25 Classrooms.
Number of Required Sensors: 25 (Temperature, Humidity, CO2).
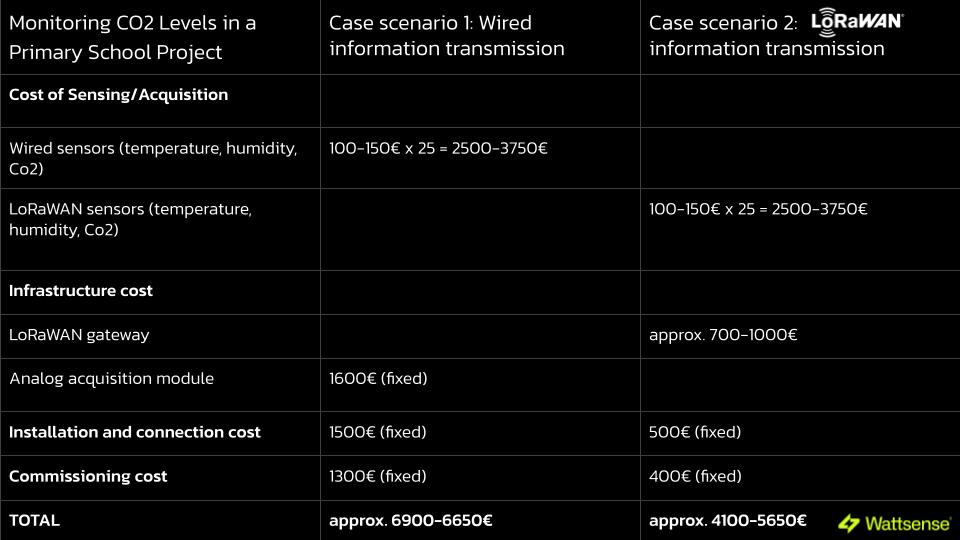
Note: It is crucial to consider maintenance and operating costs, which are nil in either case.
Regarding LoRaWAN, the main maintenance is related to battery replacement, which varies between 3 and 10 years depending on the data upload frequency requirement. In the case of wired solutions, occasional or regular interventions are necessary for various reasons, such as tightening terminals or replacing transformers.
To conclude
In summary, the adoption of wireless technologies like LoRaWAN not only accelerates ROI but also facilitates integration with existing systems and sensors. This aligns with the trend towards more interoperable and open solutions, enabling more efficient and sustainable energy management.
Using LoRaWAN technology to collect data from equipment inaccessible to wired protocols is proving to be the ideal solution. Simple to use, cost-effective and offering a wide range of equipment for every situation, LoRaWAN opens up exciting new perspectives in building automation. Don't miss this opportunity to optimize the energy efficiency and comfort of your buildings' occupants, while complying with regulatory standards.
The use of the LoRaWAN protocol in the renovation of building management systems offers an innovative technological solution tailored to the specific challenges of this field. The adoption of LoRaWAN as a connectivity protocol reflects a progressive and proactive vision for the future of building automation.
Wattsense technology makes the integration of LoRaWAN technology into buildings simple, fast and affordable. Ask for a demonstration to find out more.
Want to learn more about the Wattsense connectivity solution?
Discover our solutionContinue reading